
With Sustainable Farm Incentive (SFI) payments for establishing grass legume swards under action NUM2 there has been a lot of talk around how best to get these established within existing grass swards. In a well-balanced grass/clover sward (20-30% clover), the potential nitrogen generated through fixation by the clover nodules is equivalent to 180 kg N/ha, giving significant financial savings in manufactured fertiliser.
Top Tips getting clover established in existing grass swards:
1) Get soil conditions right before establishment
- Clover needs a soil pH of at least 6-6.2 to establish and thrive. Soil test swards prior to establishment and apply spring lime at recommended rates if required.
- Soil P and K indices should also be at index 2 or above, so correct these with fertiliser or organic manure. Clover growth can be limited in both low P & K situations.
2) Deal with weeds prior to sowing
- Weed control in grass clover swards is more difficult than in pure grass leys. Treat any weed problems before clover is introduced.
- Stich clover into established grass from 6 weeks after weed control.
- If herbicides are needed after the cover is sown, use clover safe sprays.
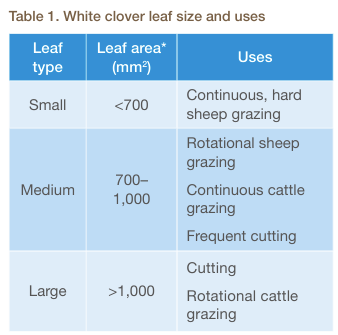
3) Choose the right plant for the job
Speak to your seed merchant about the right clover seed for your needs. Chose leaf size according to the class of the animal and the longevity of the proposed ley.
4) Introducing seed into sward
This can be done by:
- slot sleeding/direct drilling
- Broadcasting following scarification
- Hoof & tooth i.e. using animals to trample seed in and graze tight – required 20-40% bare visible soil
- Aim for 30% clover content in sward (to the visible eye this will look like 60/5 cover from above).
- Minimize competition from existing plants before sowing by heavy grazing or harrowing to open up the sward.
- Sow when the grass is least vigorous e.g. after flowering in July, as long as there is sufficient soil moisture.
- Use a higher seed rate (4.5 kg/ha or 1.5 kg/acre) to compensate for greater seedling loss
- Consider using slug pellets
5) Post sowing
- After sowing graze hard in short, intensive 3-4 day periods every month, until clover is well established, to reduce competition from other plants.
- Keep grass at 4-6cm over the winter to protect stolons from frost damage.
- Avoid excessive stolon damage through poaching.
- If clover content is too high, use intensive grazing or strategic n use to increase grass growth.
- Restrict N applications. Early growth and fixation from white clover is important to achieve a balanced sward. This means that N applications in early spring should be limited – later N applications (July/ August) should not be necessary in a clover rich sward and would discourage N fixation. Small strategic applications (up to 50 kg/N/ha) can encourage grass growth without detrimentally affecting clover growth.
Useful links:
ManagingClover2871_210310_WEB-1.pdf (projectblue.blob.core.windows.net)
White Clover Seed Guide – Germinal
